- #1
asmani
- 105
- 0
Hi all.
In the following circuit, z is an inductive load (I mean inductance + resistance).

Here is the table of cosφ measured by power factor meter in different voltages:
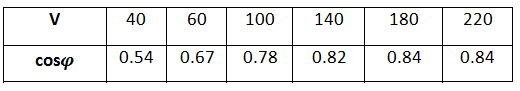
Why it's increasing? Isn't cosφ independent of the voltage of the autotransformer?
In the following circuit, z is an inductive load (I mean inductance + resistance).
Here is the table of cosφ measured by power factor meter in different voltages:
Why it's increasing? Isn't cosφ independent of the voltage of the autotransformer?